Running AI on older hardware might seem impossible, but the GTX 1070 proves it’s surprisingly capable. Thanks to quantized LLMs and tools like LM Studio, even a seven-year-old GPU can handle modern AI models locally.
While performance may not match that of cloud-based giants like GPT-5, running AI offline offers unique advantages, including enhanced privacy, offline access, and complete control over your data. In this guide, I explore how I successfully ran models like Qwen 3-4b-thinking and gpt-oss-20b on my GTX 1070, share tips for optimizing performance, and highlight the realistic limitations and impressive potential of local AI on modest hardware.
Why Use a Local AI Chatbot?
Online AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude work well—but what if you’re offline or need complete privacy? A local AI chatbot keeps all conversations and data on your device, making it ideal for sensitive work or personal use.
Privacy is the primary advantage, but local AI also offers benefits such as avoiding censorship, offline access, cost savings, and greater customization.
Read More: 7 Tech Upgrades That Backfired and Made Things Worse
What Are Quantized LLMs?
Hardware is the primary barrier to running local LLMs—powerful AI models require top-tier CPUs and GPUs, which is why most chatbots reside in the cloud. My setup is modest: an AMD Ryzen 5800X CPU, 32GB RAM, and a GTX 1070 GPU. Not cutting-edge, but sufficient for everyday use and older games.
You don’t need the biggest models to run AI locally. Quantized LLMs shrink and speed up models by simplifying the data they use, specifically the floating-point numbers. Standard AI models rely on high-precision numbers (32-bit floats), which require substantial memory and processing resources. Quantization reduces these to lower-precision formats (such as 8-bit integers), maintaining high performance while reducing storage and computational demands.
This allows older hardware, like mine, to handle smaller models—running an 8-billion-parameter quantized model instead of a massive 205B model. When OpenAI released fully quantized, open-weight reasoning models, I decided to test them on my setup—and the results were surprising.
Using a Local LLM on My GTX 1070 with LM Studio
I’m no expert on local LLMs or the software I used, but here’s how I got an AI chatbot running on my GTX 1070—and how well it performs. This guide reflects my personal setup and experience, showing that even older hardware can handle local AI surprisingly well.
Download and Install LM Studio
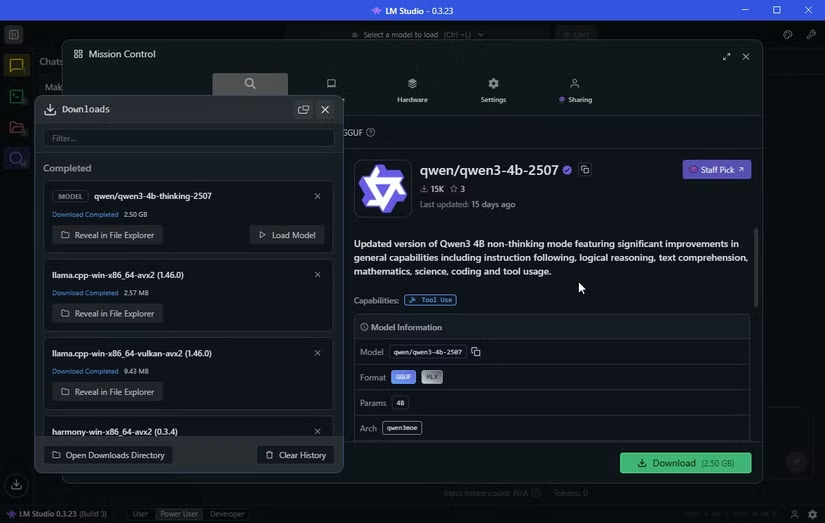
To run a local LLM, you need software like LM Studio, a free tool that lets you download and run models on your machine. Visit the LM Studio homepage and select Download for your operating system (I used Windows 10).
The installation is straightforward. Run the setup, complete the process, and launch LM Studio. For extra features, choose the Power User option, which unlocks useful settings for advanced users.
Download Your First Local AI Model
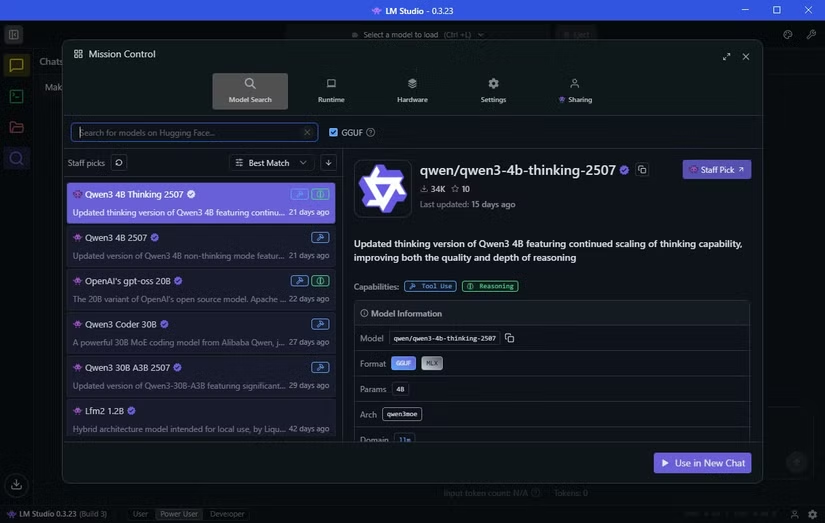
After installing LM Studio, navigate to the Discover tab (represented by a magnifying glass icon) to download your first LLM. LM Studio suggests models optimized for your hardware.
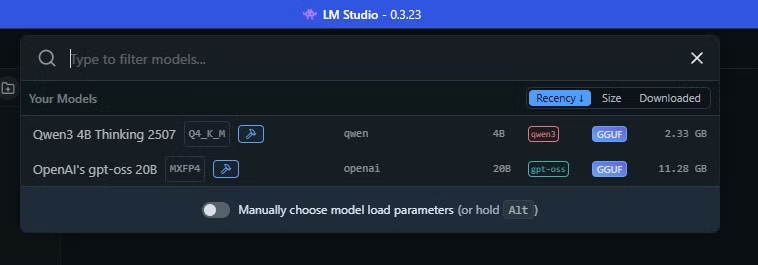
For my setup, it recommended Qwen 3-4b-thinking-2507. Developed by Alibaba, this is the third iteration of Qwen. The “4b” indicates 4 billion parameters, “thinking” means it takes extra time to generate answers, and “2507” is the last update date (25th July). At just 2.5GB, it downloads quickly. Larger models like OpenAI/gpt-oss-20b (12.11GB, 20 billion parameters) offer more powerful responses but require more resources.
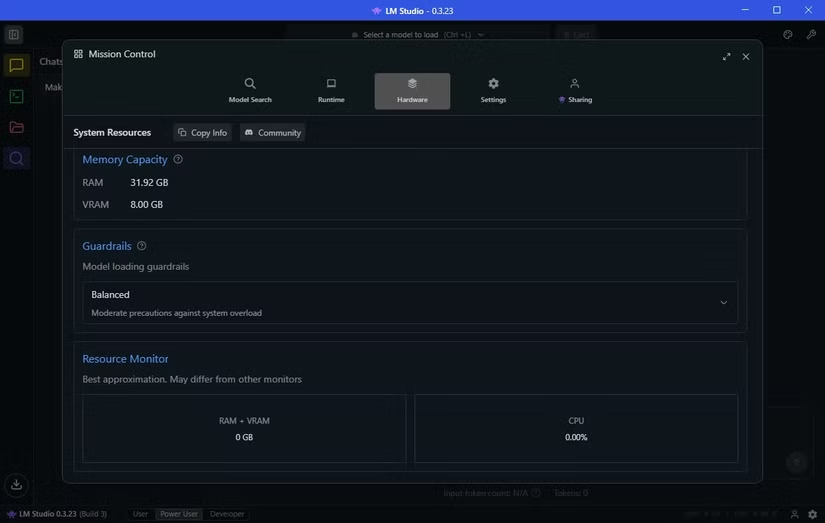
Before launching your model, switch to the Hardware tab to ensure LM Studio correctly detects your system. Adjust Guardrails to manage resource usage—mine is set to Balanced to prevent overload. The Resource Monitor under Guardrails shows real-time system usage, helping avoid crashes on limited hardware.
Load Your AI Model and Start Prompting
Now your local AI chatbot is ready. In LM Studio, use the top search bar to select your AI model. This loads it into your computer’s memory, and you can start entering prompts immediately.
Running a Local AI Model on Older Hardware: Impressive but Limited
Using a local AI model on older hardware is effective, but it has its limitations. These models aren’t as powerful as cloud-based AI, such as GPT-5, so responses may take longer and vary.
I tested classic LLM reasoning prompts on Qwen 3-4b-thinking and gpt-oss-20b. For example:
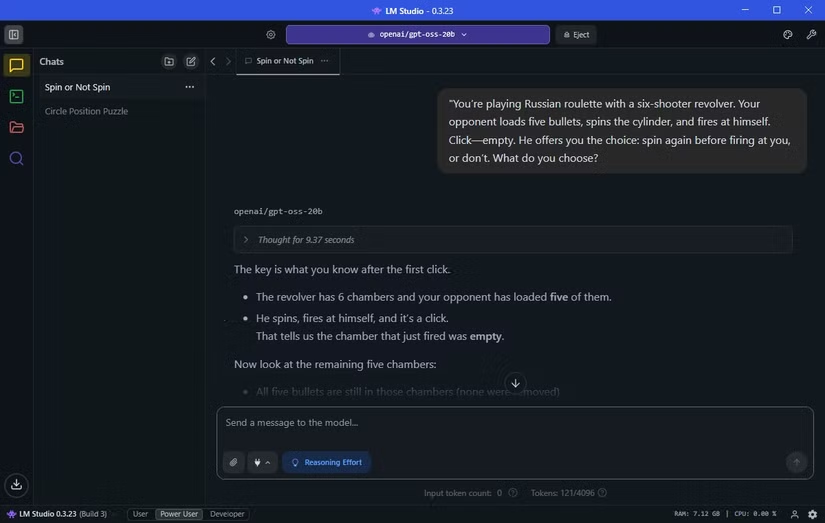
“Alan, Bob, Colin, Dave, and Emily are standing in a circle…”
Qwen solved it in 5m11s, GPT-5 took 45s, and GPT-oss-20 b completed it in just 31s. Another reasoning test, the Russian roulette puzzle, saw Qwen answer in 1m41s, GPT-5 fail, and GPT-oss-20 b respond correctly in 9 seconds.
Offline LLMs also excel in practical tasks. Asking GPT-oss to write a Snake game in Pygame produced a fully functioning game within a couple of minutes.
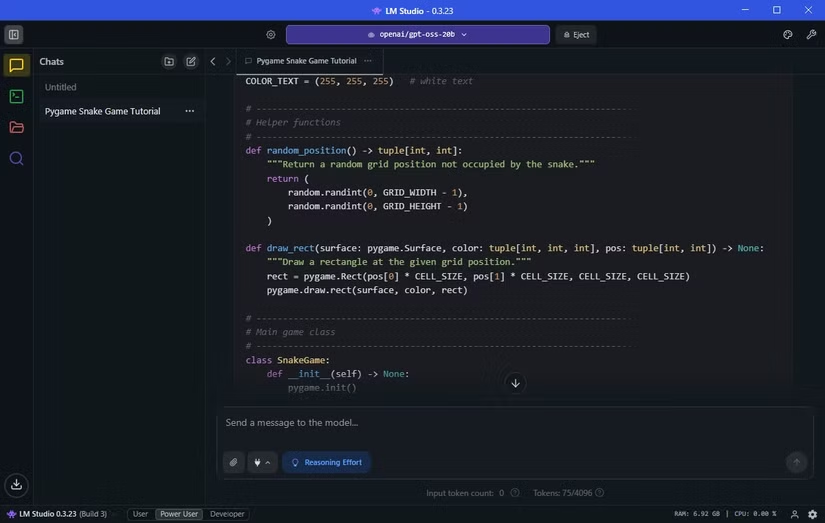
Even on modest hardware, local LLMs are surprisingly capable—but patience is required for larger reasoning tasks.
Your Old Hardware Can Run an AI Model
Running a local LLM on older hardware is all about choosing the right model. Qwen 3-4b-thinking performed well and was LM Studio’s top suggestion, but gpt-oss-20b proved faster and more accurate.
Expectations need balance, though. While GPT-OS handled prompts efficiently, my hardware can’t process massive datasets without slowing down.
Before testing, I assumed running a local AI chatbot on older hardware was impossible. Thanks to quantized models and LM Studio, it’s not only feasible—it’s surprisingly practical.
Local AI comes with trade-offs: you gain privacy, offline access, and control, but lose some speed, polish, and reasoning depth compared to cloud models like GPT-5.
Still, a seven-year-old GPU and a four-year-old CPU running modern AI is impressive. If you’ve hesitated due to hardware limits, quantized local models offer a compelling entry into offline AI.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I run modern AI models on a GTX 1070?
Yes! Using quantized LLMs, older GPUs like the GTX 1070 can run local AI models efficiently, though larger models may require longer processing times.
What is a quantized LLM?
A quantized LLM is a compressed AI model that utilizes lower-precision numbers to reduce memory and computational requirements, enabling it to run on modest hardware with minimal loss of accuracy.
Which local AI models work best on older hardware?
Smaller models, such as Qwen 3-4b-thinking or GPT-3.5 B, are ideal for older GPUs. They balance performance with resource requirements.
Do I need special software to run a local AI model?
Yes. Tools like LM Studio enable you to download, manage, and run local LLMs on your machine without requiring internet access.
What are the limitations of running AI locally on older hardware?
Expect slower response times, reduced reasoning speed, and limits on handling very large datasets. Cloud-based models, such as GPT-5, are still faster and more polished.
Why use a local AI model instead of a cloud-based one?
Local AI offers privacy, offline access, and full control over your data, making it ideal for sensitive information or situations without internet connectivity.
Can I utilize local AI for practical tasks, such as coding or gaming?
Absolutely. Even older GPUs can run models capable of generating code, small games, or handling reasoning tasks, though larger or more complex projects may be slower.
Conclusion
Running a local AI model on older hardware, such as a GTX 1070, is not only possible but surprisingly practical, thanks to quantized LLMs and tools like LM Studio. While performance may not match that of cloud-based AI like GPT-5, local models offer privacy, offline access, and control over your data.
With the right model selection and setup, even modest GPUs and CPUs can handle modern AI tasks—from reasoning prompts to coding small projects—making offline AI accessible to more users than ever.